Blood Urea Nitrogen and Creatinine
Key Indicators of Renal Health.
When combining these two tests Clinicians can reliably gauge the renal health of their patients. It is important to measure both BUN and creatinine when diagnosing Acute Kidney Injury. For ICU patients – accurate and fast BUN and Creatinine testing is the key to diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
AKI is a sudden kidney damage that occurs within a few hours or days as metabolic wastes and fluid accumulate in the body. More common in ICU patients, especially older patients with underlying diseases that cause poor renal perfusion, it affects 5–10% of all hospitalized and 30–50% of ICU patients, the mortality rate often exceeds 50% in the ICU setting.
Unlike kidney failure, AKI is reversible if it is found in time and treated immediately.
“Exposures known to produce AKI in susceptible populations include sepsis, ischemia, heart failure, liver disease, major surgery (especially vascular and cardiac), myonecrosis, urinary tract obstruction, and various nephrotoxins.”1
“In the critically ill, sepsis is the major cause of AKI, accounting for nearly 50% of cases. Several studies have reported that sepsis induced AKI is associated with short- and long-term risk of death.” 1
“It has become very clear that patients, especially patients in the ICU, are dying of AKI and not just simply with AKI. Even small changes in serum creatinine concentrations are associated with a substantial increase in the risk of death.” 1
References:
- Kai Singbartl and John A. Kellum. AKI in the ICU: definition, epidemiology, risk stratification, and outcomes, Kidney Int. 2012 May;81(9):819-25.
Creatinine
Creatinine is a metabolic byproduct produced by the breakdown of creatine in muscle, released into the blood stream, freely filtered and not reabsorbed by the kidneys and therefore found in the urine. It is produced at a steady rate and not typically affected by diet or exercise and therefore may be used to establish a baseline for renal function.
Measurement of Creatinine in the blood and the urine (collected over a 24hr period) allows for the calculation of creatinine clearance which is synonymous with glomerular filtration rate, an indicator of kidney function, estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate using various formulas can be used to assess Renal function with a simple blood test.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
BUN is primarily a measurement of urea nitrogen in the blood produced by the breakdown of proteins and can be used as a test of renal function. It is produced in the liver and excreted by the kidneys.
BUN to Creatinine Ratio
The ratio of BUN (mg/dL) to plasma creatinine (mg/dL) is used to determine the cause and type of AKI.
A single creatinine test may tell if the patient has AKI, but without BUN you cannot tell the type of AKI, if it is post-, renal or pre-renal. An increased ratio may be due to conditions that cause a decrease in blood flow to the kidneys, such as congestive heart failure or dehydration. It may also be seen with increased protein from gastrointestinal bleeding or increased protein in the diet. The ratio may be decreased with liver disease (due to decrease in the formation of urea) and malnutrition.
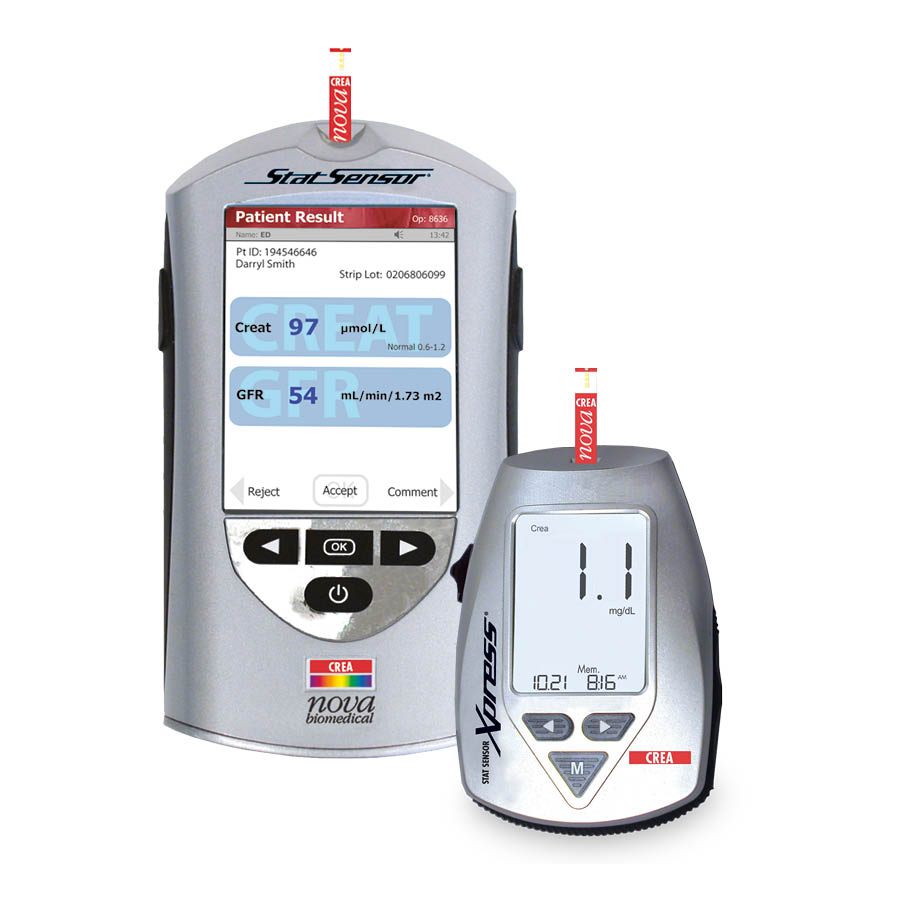
Measure creatinine and BUN with following analyzer:
- 22 measured parameters
- Including iMg, BUN and creatinine
- Reliable and precise results
- Extensive connectivity options
- Automated QC system